Imagine that you’re at your favourite clothing store, and while trying a new pair of jeans, the salesperson suggests a stylish belt and a matching jacket that would elevate your look. You hadn’t planned on buying anything else, but the combo makes perfect sense, and you walk out with an upgrade to your wardrobe. That’s cross-selling!
Cross-selling is a powerful sales strategy that can significantly boost revenue and enhance customer relationships. However, if approached incorrectly, it can backfire. This blog discusses effective techniques that anyone who interacts with a customer can use.
Key takeaways
What is cross‑selling: Offering additional, complementary products or services to customers alongside their initial purchase (e.g., phone case with a new phone, analytics add‑on for a SaaS tool).
Benefits of effective cross‑selling: Increases revenue, boosts customer loyalty, differentiates your brand, enhances profitability through bundled offers, and generates valuable referrals.
Risks to avoid: Overdoing it can seem pushy, erode trust, confuse B2B clients if introduced too early, or hurt margins via excessive discounting.
Key techniques:
Bundle related products at a discount
Use personalized suggestions based on purchase history
Educate customers on added value
Apply point-of-sale suggestions, loyalty incentives, targeted emails, and exclusive offers.
Who should cross‑sell: It’s a shared responsibility—sales reps, customer success managers, support staff, marketing teams, and e‑commerce systems can all participate.
Best practices for cross-selling:
Listen to and understand customer needs
Recommend only one or two well-matched items
Focus on value—not price
Be honest and transparent
Avoid being pushy
Follow up post‑purchase to highlight further benefits
What is cross-selling?
Cross-selling is a sales strategy where a company encourages customers to purchase additional products or services that complement or enhance their original purchase. The goal is to increase the value of a sale and provide more solutions to the customer.
An example in a retail environment is when your barista asks if you would you like a muffin or a sandwich with your coffee or you are offered accessories like a phone case, screen protector, or wireless earbuds when you purchase a new smartphone.
In a SaaS environment, cross-selling might involve offering premium analytics tools that deliver deeper insights and reporting features, integrations with CRM, or communication platforms to enhance the workflow or a premium customer support package or training programs to help the customer maximize the use of the software.
Cross-selling is not about pushing extra products—it’s about enhancing the customer’s experience by offering complementary items.
Why invest in cross-selling?
According to research, acquiring a new customer costs six to seven times more than retaining an existing one. This is why it is essential to care for your current customers and actively explore opportunities to grow how much your existing client base spends on your organization (customer lifetime value).
The first benefit of cross-selling is increased revenue. By offering additional products that complement the original purchase, you can enhance customer interactions and maximize the revenue from each contact.
It can also strengthen customer loyalty by solving customers’ problems with relevant solutions. When customers feel that you are genuinely addressing their needs rather than just trying to sell more, it builds trust and reinforces their loyalty to your brand.
Businesses can also differentiate themselves with cross-selling. A well-executed service or product management strategy that delivers options to add value to the customer experience enables you to stand out from competitors.
Another advantage is that cross-selling can generate more leads from satisfied, loyal customers who are more likely to refer your products or services.
Finally, cross-selling can lead to improved profitability, even when individual product or service prices are lowered through discounts. Bundling can still result in higher overall profit than selling just one at a higher margin.
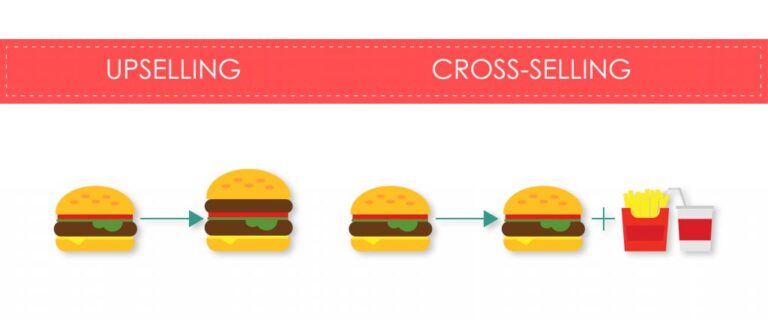
Difference between cross-selling and upselling
Cross-selling and upselling are both sales strategies that encourage customers to spend more.
For example, when working with an HVAC company, cross-selling involves recommending a smart thermostat, air purifier, or routine maintenance package to go along with their new AC unit, enhancing the overall system’s performance and longevity. Upselling would be persuading the customer to purchase a more advanced or premium model, like a high-efficiency furnace or A/C system with better energy savings, more features, or a longer warranty.
Taking the example of a bank, cross-selling would be offering home insurance, investment services of a savings plans to a customer who takes out a mortgage. Upselling would be offering a premium credit card with travel rewards or higher credit limit for a customer who applies for a basic credit card.
Source: varstreetinc.com
Potential drawbacks of cross-selling
One of the main challenges of cross-selling is that it can make a company appear self-serving. When the focus shifts from solving the customer’s problems to pushing one product after another, customers may feel that the business is more interested in making a sale than addressing their needs. It’s important to ensure that cross-selling is aligned with the customer’s agenda and addresses their problems, one at a time.
Another potential drawback of ineffective cross-selling is that it can erode trust and loyalty. If a customer senses that interactions are primarily transactional, focused on the “next product up,” this can create a win-lose scenario where the customer feels like they’re being pushed into buying rather than engaging in a partnership. This approach not only damages trust but also reduces the likelihood that the customer will continue doing business or refer others.
In complex B2B sales, where the buying process can be lengthy and involved, introducing a second product too quickly can introduce confusion. Customers who have invested significant time and resources into purchasing one product may feel disoriented if a new offering is introduced too soon. This can detract from the perceived value of the initial product, making it harder for the customer to see the connection between the additional offering and their needs.
Lastly, cross-selling can hurt profitability if not handled strategically. While it has the potential to increase profits, businesses that struggle to articulate their value often resort to bundling products at deep discounts to win customers. This can erode margins and set an expectation that future products will also be discounted, ultimately commoditizing the offering. This cycle of discounting reduces the potential for long-term profitable partnerships with customers.
To avoid these pitfalls, companies need to focus on timing, customer understanding, and value-driven conversations. With the right approach, cross-selling can be a powerful tool for both enhancing customer satisfaction and driving business growth.
Techniques to effectively cross-sell
Cross-selling techniques are strategies that encourage clients to purchase related products. Here are common methods for cross-selling:
- Bundling: Offer multiple products together as a package at a discounted rate.
- Personalized recommendations or “related products”: Use customer data, including data on past customers’ purchases, to suggest personalized products that align with their needs.
Education and awareness: Inform customers about the value and benefits of related products they may not know.
Point-of-sale cross-selling: During key moments in the customer journey (e.g., account sign-ups or loan applications), suggest additional services that complement their current product.
Loyalty or reward programs: Use points and discounts to encourage customers to explore other products.
Targeted email campaigns: Use segmented email marketing that is personalized and based on the customer’s behaviour to promote relevant products to existing customers.
Exclusive offers: Offering exclusive discounts, limited-time deals, or first access to existing customers for new products that motivate them to explore additional services.
Who is responsible for cross-selling?
Cross-selling can be done by anyone involved in sales or customer service. Key individuals and touchpoints who should focus on cross-selling include:
Sales reps and retail staff are well-positioned to suggest additional products during sales, especially when they understand the customer’s needs.
Customer success, account managers, and relationship managers with a deep understanding of a client’s needs can identify when another product would better meet that need.
Customer service reps or technical support teams can identify opportunities to suggest other products when resolving issues that could better suit the customer.
Marketing teams, through email campaigns, can offer personalized offers and loyalty programs.
E-commerce platforms and digital managers can configure systems to suggest other products with “Customers also bought” features or pop-ups with offers in mobile apps.
Cross-selling tips
Like in upselling, cross-selling has to be done carefully. You want to deliver value while maintaining customer satisfaction. Here are some tips to effectively cross-sell:
Understand the customer’s needs: Listen carefully and understand the customer’s preferences and pain points before making any suggestions.
Recommend complementary products: Ensure that the products or services you suggest complement the customer’s original purchase.
Leverage timing: Cross-sell when the customer is already in a purchasing mindset but not overwhelmed.
Highlight the value, not the price: Explain how the other products or services will meet their needs, save time, or last longer.
Use bundling, discounts and offers: Group products at a discounted rate that offers additional value.
Leverage social proof: Use testimonials, reviews, or success stories from other customers who benefited from the cross-sell.
Use past customer data: Use the data from your loyalty program or other customer purchase patterns to recommend other interesting products.
Keep it simple: Present one or two relevant suggestions that improve their purchase-don’t overwhelm the customer!
Be honest and transparent: Always be upfront about the costs and benefits of the cross-sell.
Don’t be pushy: An aggressive approach can turn off customers and damage the relationship. Let the customer feel in control of their decision.
Follow-up after purchase: Call, text or email the customer after their initial purchase to suggest additional items that may enhance their experience.
How LEAi supports cross-selling
LEAi is an AI-powered tool for creating training content and supports cross-selling in several key ways:
- Educating on other products and services: Create training content that helps front-line staff and customers better understand the company’s other products or services.
- Content for cross-selling: Generate training and informational content highlighting related products or complementary services and how they can enhance their current solution.
- Build training to show synergy: Develop training content that shows customers how multiple products work together to solve problems or provide more value.
- Addressing common objections: Create learning modules or guides that help front-line staff address customers’ objections about upgrading and how to overcome resistance.
- Continuous learning and customer engagement: Generate continuous learning programs that keep customers engaged with products and services and subtly guide customers toward cross-sell opportunities.
Contact us if you want to incorporate training, videos, and other guides to help your sales and customer success teams cross-sell.




